Understanding of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Gateways
In this article, we’ll discuss Gateways and what various types of Gateways exist in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
What is Gateway
A Gateway is a network component that allows data to flow from one network to another.
A Gateway is a gate between two networks (for example OCI to Internet, OCI Compute Instance to on-premises NW, etc.)
Gateways serve as an entry and exit point for a network as all data going outside of a network must pass through it.
Types of Gateway:
The following 5 types of GW exist in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure:
- Internet Gateway
- NAT Gateway
- Service Gateway
- Dynamic Routing Gateway
- Local Peering Gateway
What is Internet Gateway
Internet Gateway provides the public subnet direct access to public endpoints on the internet.
Connections can be initiated from the subnet or from the internet
The resources in the public subnet must have public IP addresses.
Only one IGW is allowed per VCN.
Each public subnet that needs to use the IGW must have a route table rule that specifies Internet Gateway as the target.

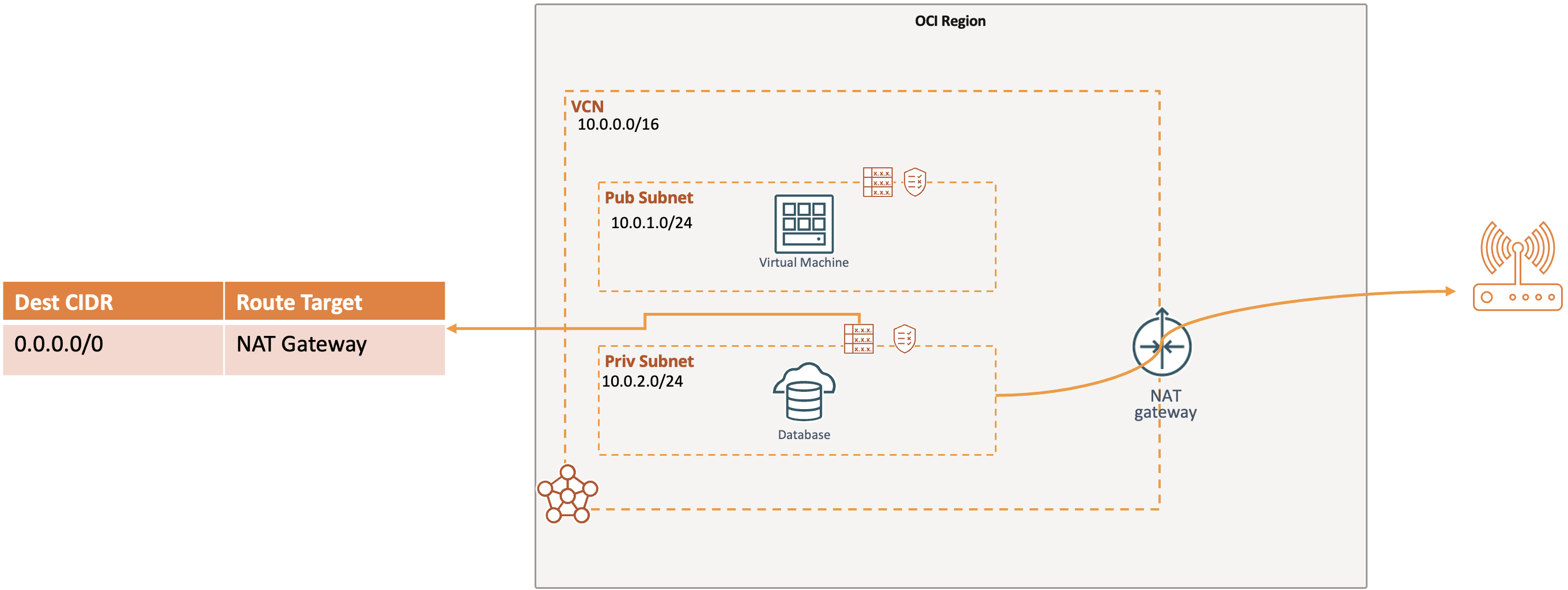
What is NAT Gateway
NAT Gateway provides the private subnet direct access to public endpoints on the internet.
Connections can be initiated from the subnet only (uni-directional).
NAT Gateway is basically used to download Patches or other updates from the internet.
OCI resources are not required to be in the public subnet in order to access the internet.
What is Service Gateway (SGW)
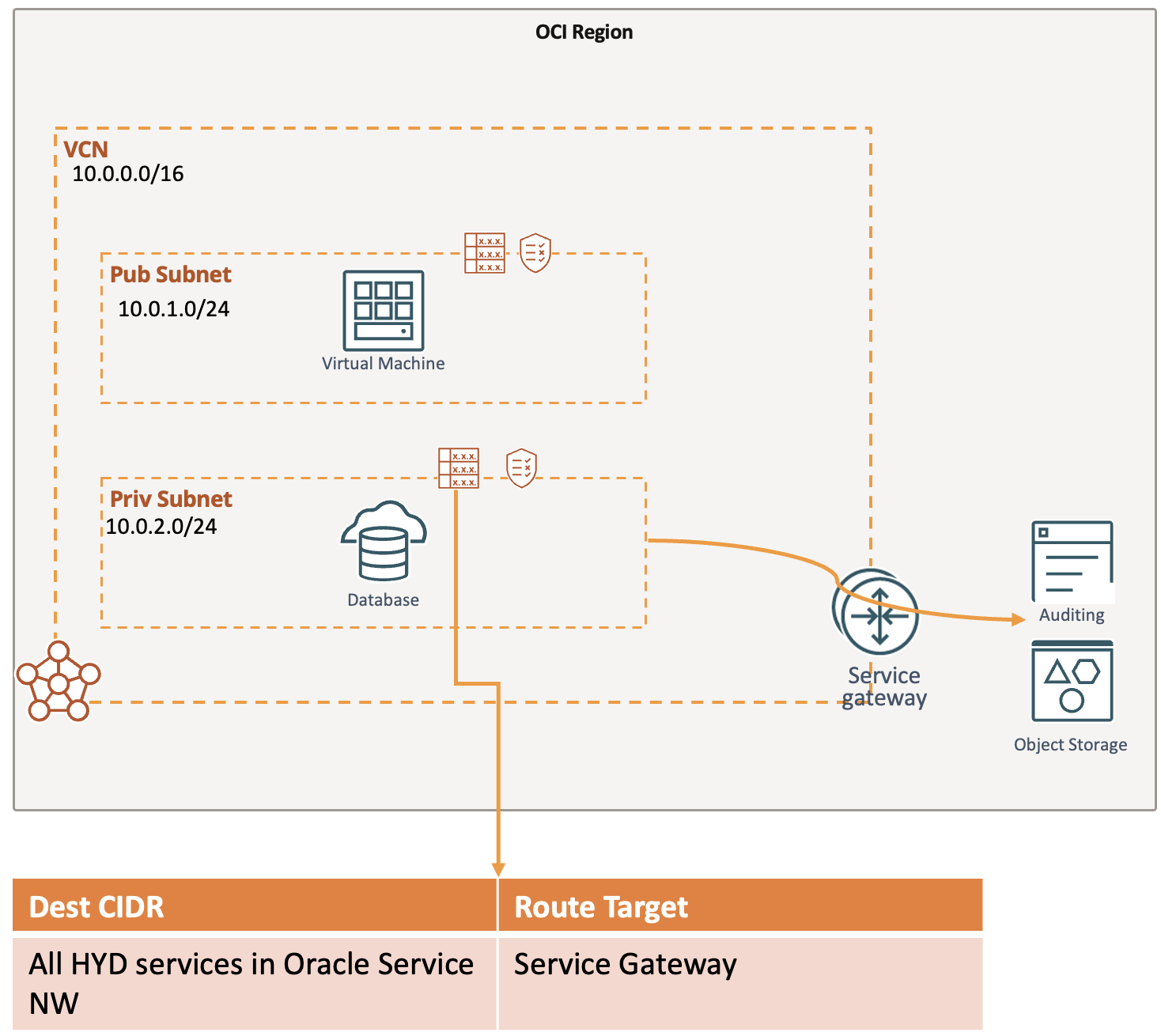
Service Gateway lets resources in VCN access public OCI Service (Ex Object Storage, Oracle Integration, etc) but without using the internet (IGW or NAT GW).
Routing travels over OCI Network fabric and never traverses over the internet.
Connections can be initiated only from the subnet (uni-directional).
What is Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG)
A Dynamic Routing Gateway acts as a virtual router, that provides a path for traffic between your on-premises networks and VCNs and can also be used to route traffic between two VCNs (in different regions).
For On-Premise connection, we can use:
- VPN Connect
- FastConnect
DRG is a standalone Object & must be Attached to VCN.

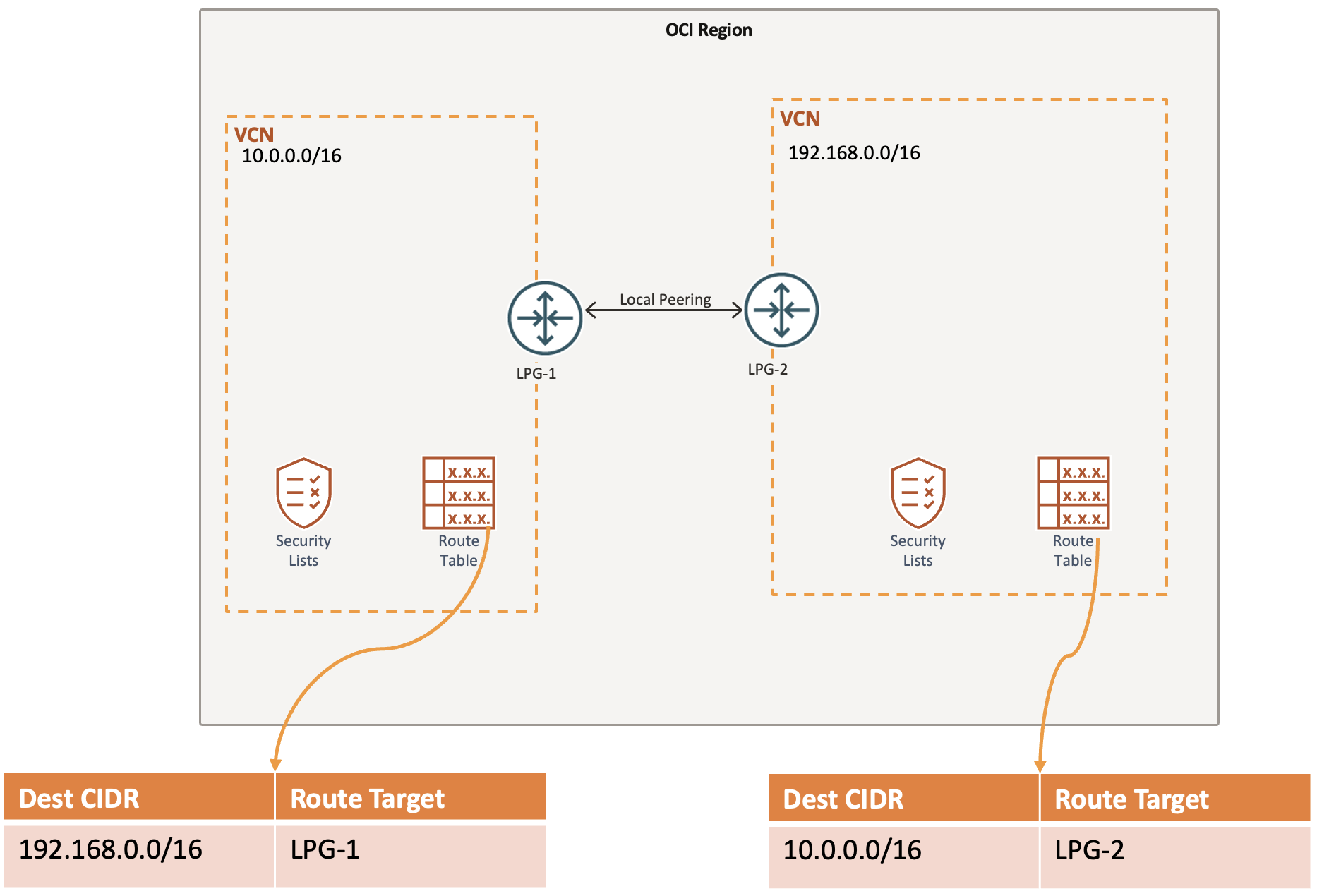
What is Local Peering Gateway (LPG)
Local Peering Gateway allows to communicate between two VCNs within the same region.
Two VCNs can’t have overlapping CIDRs.
You have to create LPG at the VCN level.
Configure route table in respective subnets.
For further details, you can refer to the following detailed video:
Hope you find this article and video useful and relevant. Please like, comment, and share the video and subscribe to our YouTube channel to get such amazing content.
Further Readings
How to create uses and groups in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
The compartments in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
How to create policies in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
How to Create Virtual Cloud Network in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure



